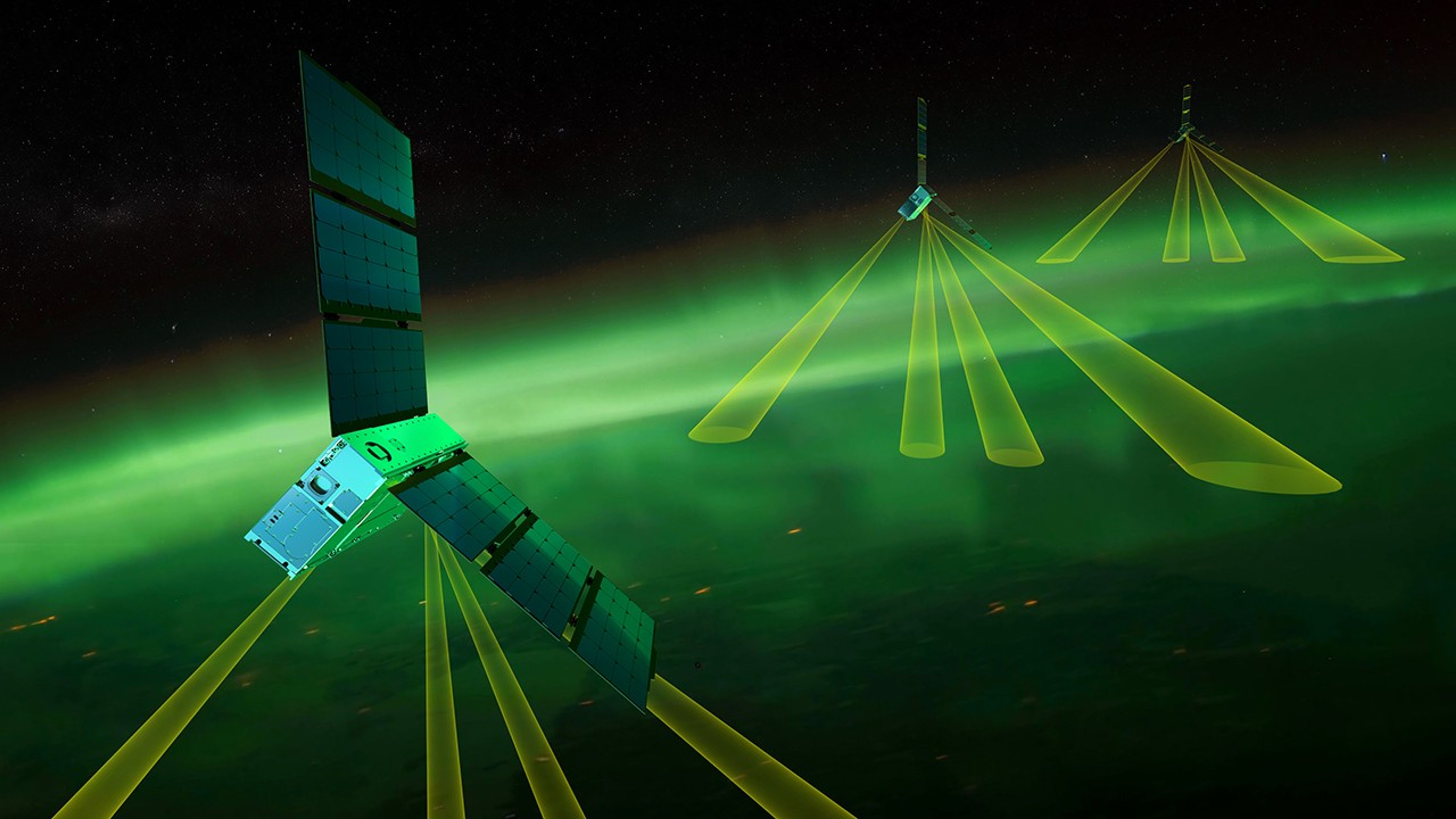
Under the nighttime California sky, NASA’s EZIE (Electrojet Zeeman Imaging Explorer) mission launched aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket at 11:43 p.m. PDT on March 14.
Taking off from Vandenberg Space Force Base near Santa Barbara, the EZIE mission’s trio of small satellites will fly in a pearls-on-a-string configuration approximately 260 to 370 miles above Earth’s surface to map the auroral electrojets, powerful electric currents that flow through our upper atmosphere in the polar regions where auroras glow in the sky.
At approximately 2 a.m. PDT on March 15, the EZIE satellites were successfully deployed. Within the next 10 days, the spacecraft will send signals to verify they are in good health and ready to embark on their 18-month mission.
“NASA has leaned into small missions that can provide compelling science while accepting more risk. EZIE represents excellent science being executed by an excellent team, and it is delivering exactly what NASA is looking for,” said Jared Leisner, program executive for EZIE at NASA Headquarters in Washington.
The electrojets — and their visible counterparts, theauroras — are generated duringsolar storms when tremendous amounts of energy get transferred into Earth’s upper atmosphere from the solar wind. Each of the EZIE spacecraft will map the electrojets, advancing our understanding of the physics of how Earth interacts with its surrounding space. This understanding will apply not only to our own planet but also to any magnetized planet in our solar system and beyond. The mission will also help scientists create models for predicting space weather to mitigate its disruptive impacts on our society.
“It is truly incredible to see our spacecraft flying and making critical measurements, marking the start of an exciting new chapter for the EZIE mission,” said Nelli Mosavi-Hoyer, project manager for EZIE at the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland. “I am very proud of the dedication and hard work of our team. This achievement is a testament to the team’s perseverance and expertise, and I look forward to the valuable insights EZIE will bring to our understanding of Earth’s electrojets and space weather.”
Instead of using propulsion to control their polar orbit, the spacecraft will actively use drag experienced while flying through the upper atmosphere to individually tune their spacing. Each successive spacecraft will fly over the same region 2 to 10 minutes after the former.
“Missions have studied these currents before, but typically either at the very large or very small scales,” said Larry Kepko, EZIE mission scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “EZIE will help us understand how these currents form and evolve, at scales we’ve never probed.”
The mission team is also working to distribute magnetometer kits called EZIE-Mag, which are available to teachers, students, and science enthusiasts who want to take their own measurements of the Earth-space electrical current system. EZIE-Mag data will be combined with EZIE measurements made from space to assemble a clear picture of this vast electrical current circuit.
The EZIE mission is funded by the Heliophysics Division within NASA’s Science Mission Directorate and is managed by the Explorers Program Office at NASA Goddard. The Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory leads the mission for NASA. Blue Canyon Technologies in Boulder, Colorado, built the CubeSats, and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California built the Microwave Electrojet Magnetogram, which will map the electrojets, for each of the three satellites.
For the latest mission updates, follow NASA’s EZIE blog.
By Brett Molina
Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory