NASA’s Webb Explores Largest Star-Forming Cloud in Milky Way

Image: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Adam Ginsburg (University of Florida), Nazar Budaiev (University of Florida), Taehwa Yoo (University of Florida); Image Processing: Alyssa Pagan (STScI)
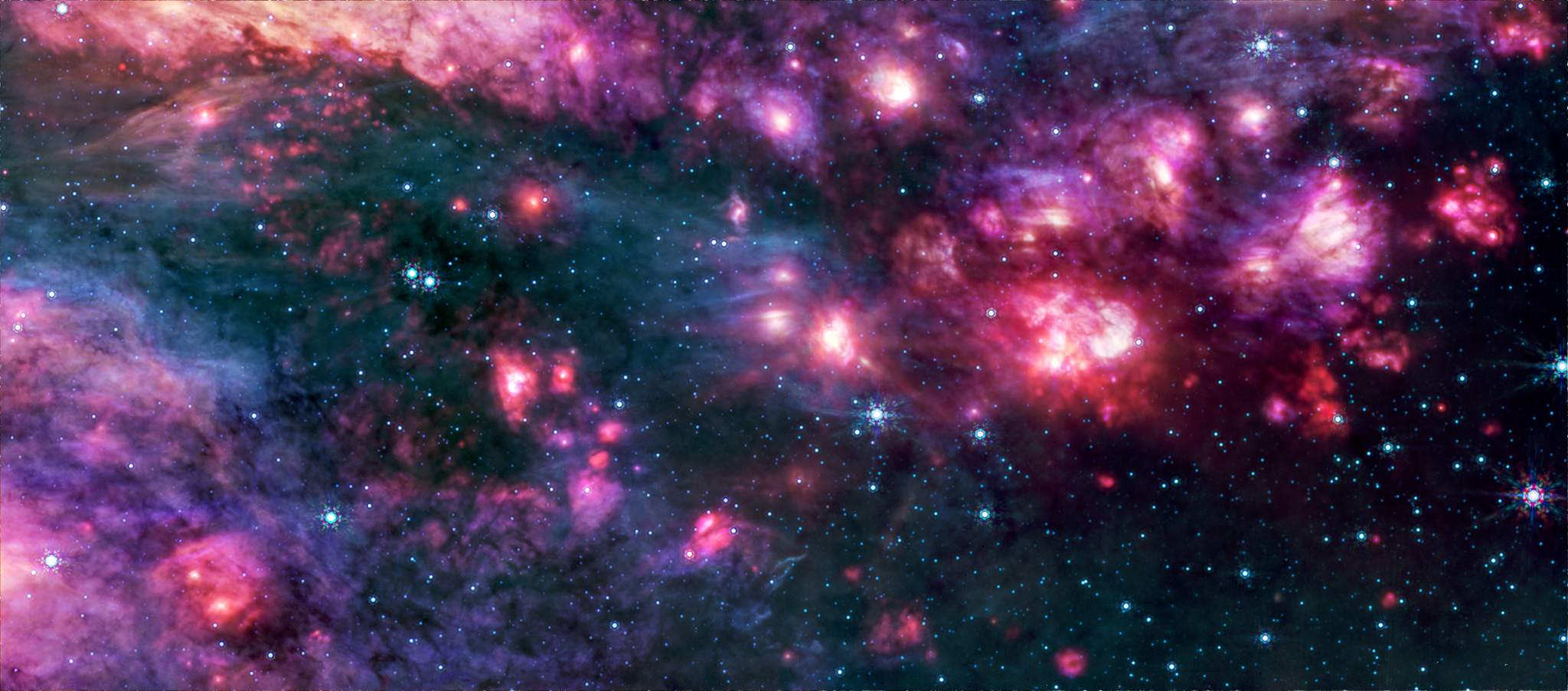
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has revealed a colorful array of massive stars and glowing cosmic dust in the Sagittarius B2 molecular cloud, the most massive and active star-forming region in our Milky Way galaxy.
“Webb’s powerful infrared instruments provide detail we’ve never been able to see before, which will help us to understand some of the still-elusive mysteries of massive star formation and why Sagittarius B2 is so much more active than the rest of the galactic center,” said astronomer Adam Ginsburg of the University of Florida, principal investigator of the program.
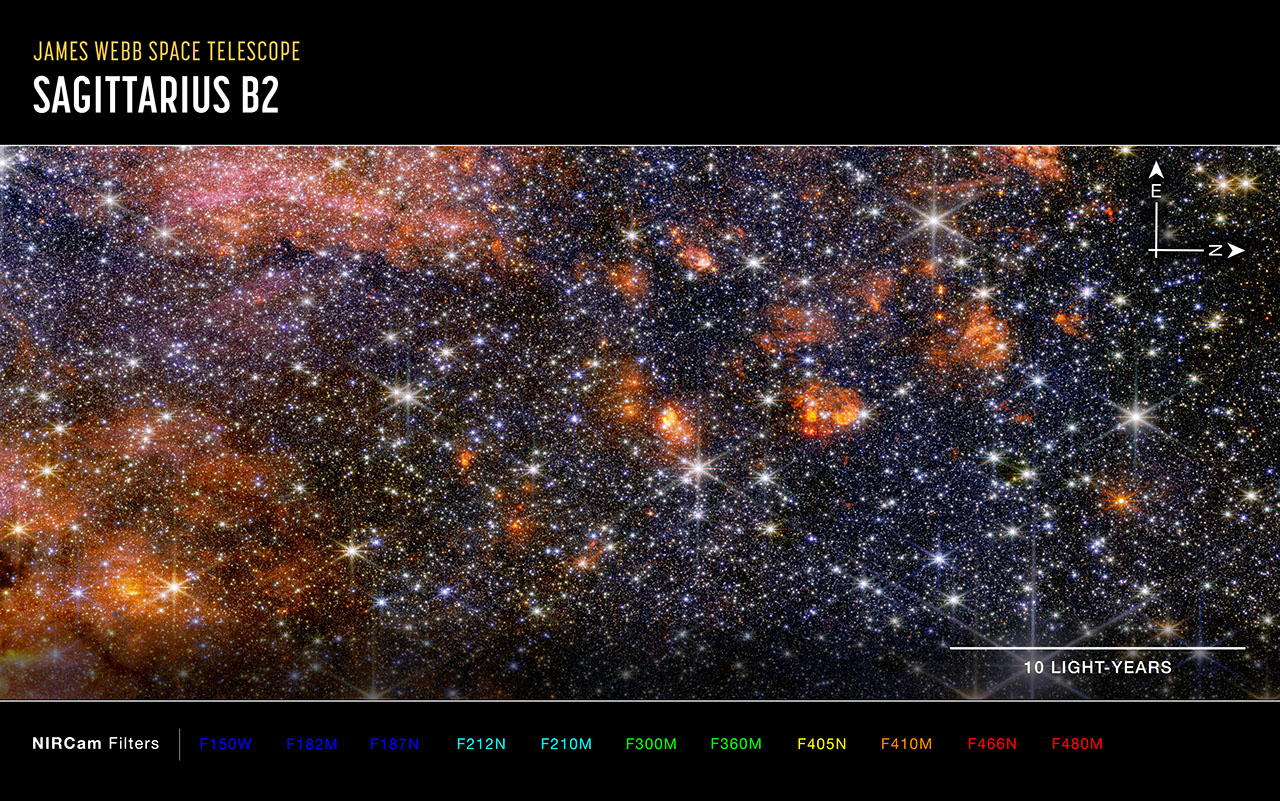
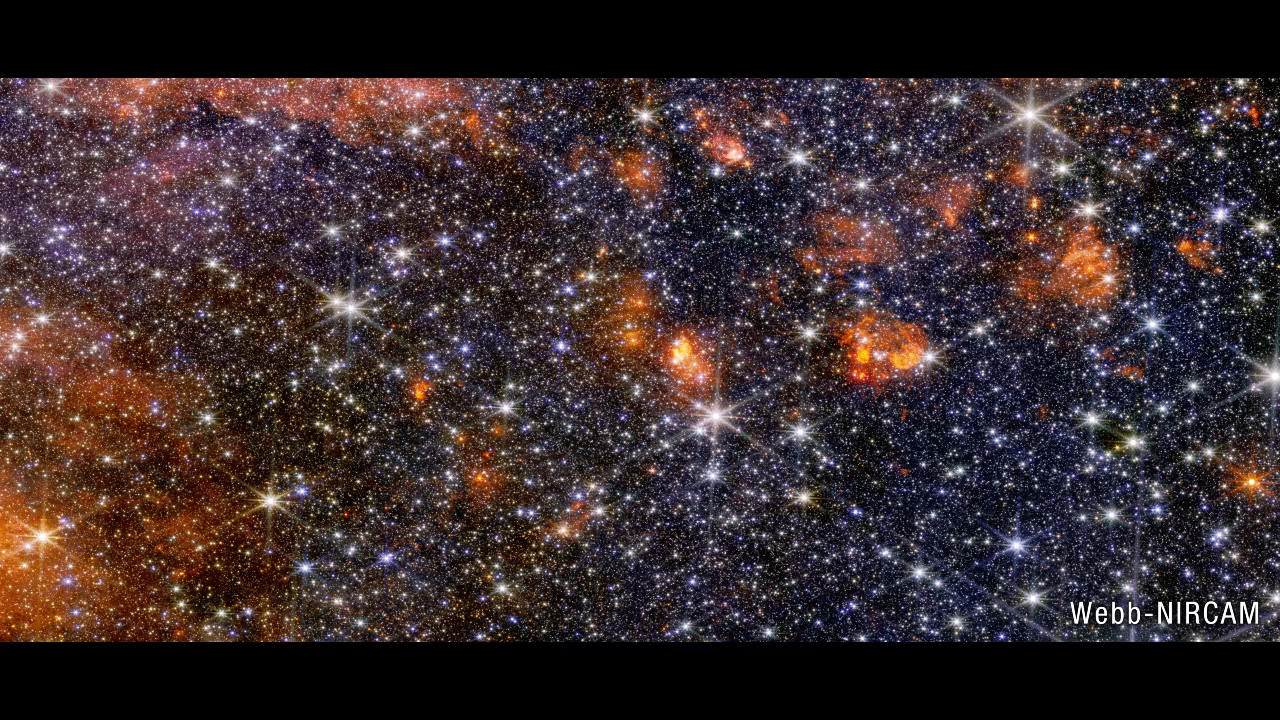
Image A: Sagittarius B2 (NIRCam Image)

Sagittarius B2 is located only a few hundred light-years from the supermassive black hole at the heart of the galaxy called Sagittarius A*, a region densely packed with stars, star-forming clouds, and complex magnetic fields. The infrared light that Webb detects is able to pass through some of the area’s thick clouds to reveal young stars and the warm dust surrounding them.
However, one of the most notable aspects of Webb’s images of Sagittarius B2 are the portions that remain dark. These ironically empty-looking areas of space are actually so dense with gas and dust that even Webb cannot see through them. These thick clouds are the raw material of future stars and a cocoon for those still too young to shine.
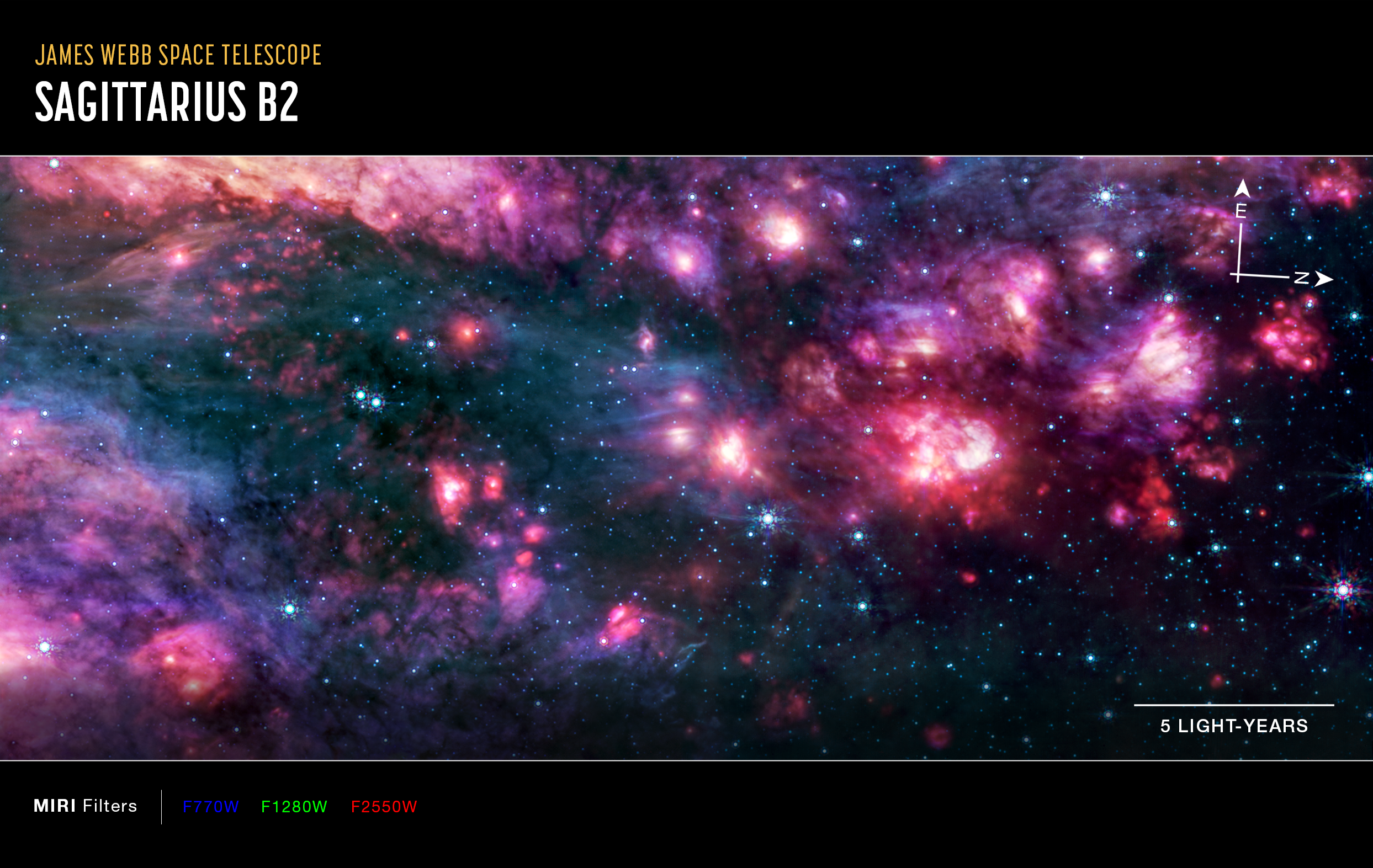
The high resolution and mid-infrared sensitivity of Webb’s MIRI (Mid-Infrared Instrument) revealed this region in unprecedented detail, including glowing cosmic dust heated by very young massive stars. The reddest area on the right half of MIRI’s image, known as Sagittarius B2 North, is one of the most molecularly rich regions known, but astronomers have never seen it with such clarity. (Note: North is to the right in these Webb images.)
Image B: Sagittarius B2 (MIRI Image)

The difference longer wavelengths of light make, even within the infrared spectrum, are stark when comparing the images from Webb’s MIRI and NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) instruments. Glowing gas and dust appear dramatically in mid-infrared light, while all but the brightest stars disappear from view.
In contrast to MIRI, colorful stars steal the show in Webb’s NIRCam image, punctuated occasionally by bright clouds of gas and dust. Further research into these stars will reveal details of their masses and ages, which will help astronomers better understand the process of star formation in this dense, active galactic center region. Has it been going on for millions of years? Or has some unknown process triggered it only recently?
Image C: Compare NIRCam and MIRI Images of Sagittarius B2




NIRCam
MIRI
Compare NIRCam and MIRI Images of Sagittarius B2
Astronomers hope Webb will shed light on why star formation in the galactic center is so disproportionately low. Though the region is stocked with plenty of gaseous raw material, on the whole it is not nearly as productive as Sagittarius B2. While Sagittarius B2 has only 10 percent of the galactic center’s gas, it produces 50 percent of its stars.
“Humans have been studying the stars for thousands of years, and there is still a lot to understand,” said Nazar Budaiev, a graduate student at the University of Florida and the co-principal investigator of the study. “For everything new Webb is showing us, there are also new mysteries to explore, and it’s exciting to be a part of that ongoing discovery.”
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
To learn more about Webb, visit:
Related Information
Read more: NASA’s Webb Reveals New Features in Heart of Milky Way
Explore: ViewSpace interactive image tour of the center of the Milky Way
Explore: ViewSpace interactive views of the Eagle Nebula in different forms of light
Read more: Webb’s Star Formation Discoveries
Read more: Star formation in the Cat’s Paw Nebula
Related For Kids
En Español
Related Images & Videos

Sagittarius B2 NIRCam to MIRI Fade
See what different wavelengths of infrared light reveal and conceal. Near-infrared light, which is nearest to visible red, comes from some gas and an abundance of colorful stars. The longer wavelengths of mid-infrared light are emitted by warm dust and only the brightest stars….
Share
Details
Laura Betz
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
laura.e.betz@nasa.gov
Leah Ramsay
Space Telescope Science Institute
Baltimore, Maryland
Christine Pulliam
Space Telescope Science Institute
Baltimore, Maryland