4 min read
Curiosity Blog, Sols 4577-4579: Watch the Skies
Written by Deborah Padgett, OPGS Task Lead at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory
Earth planning date: Friday, June 20, 2025
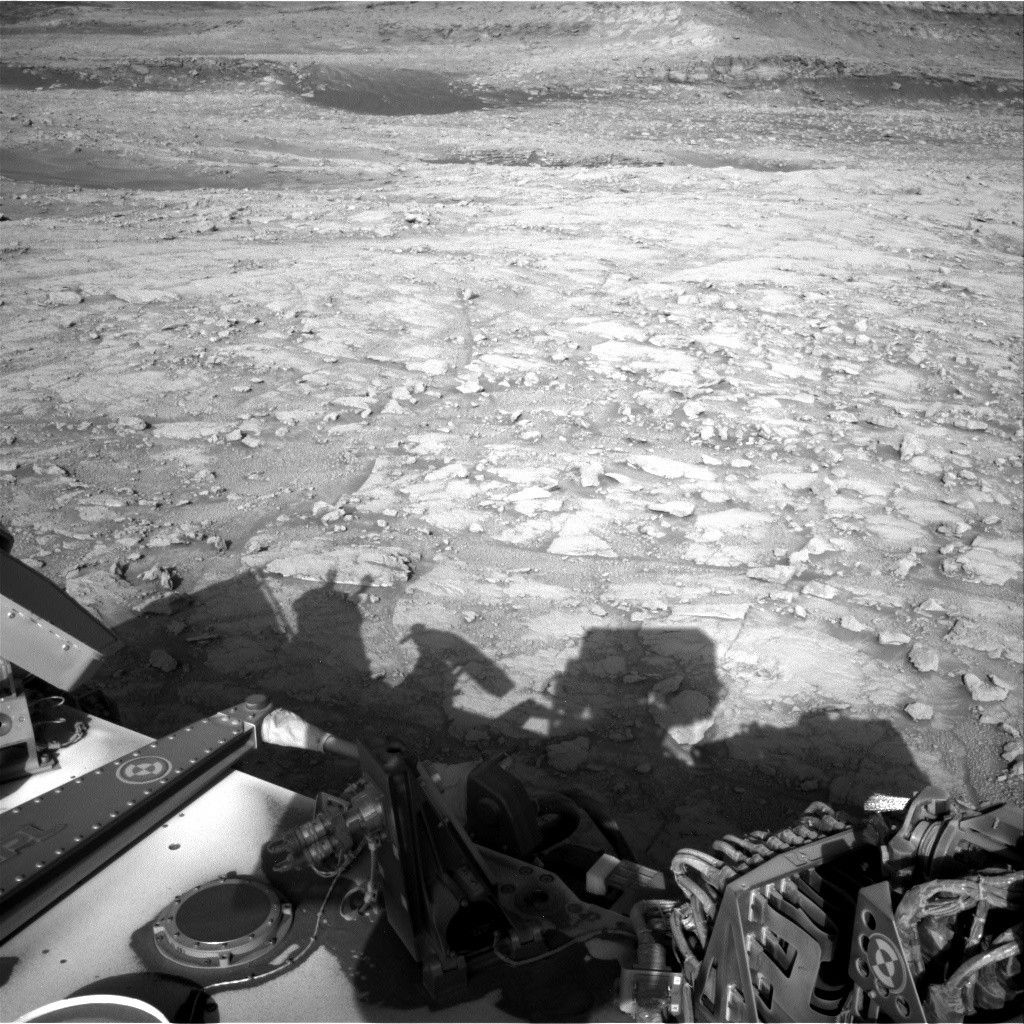
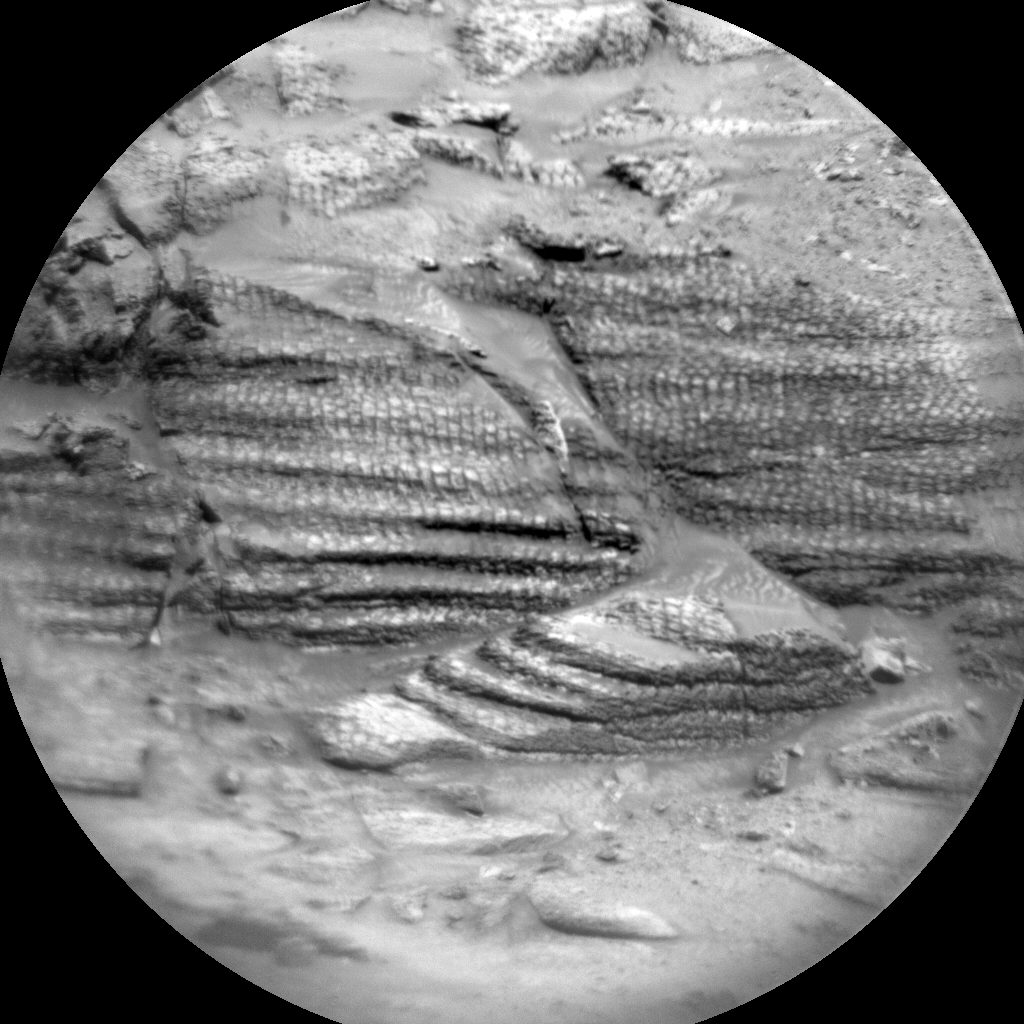
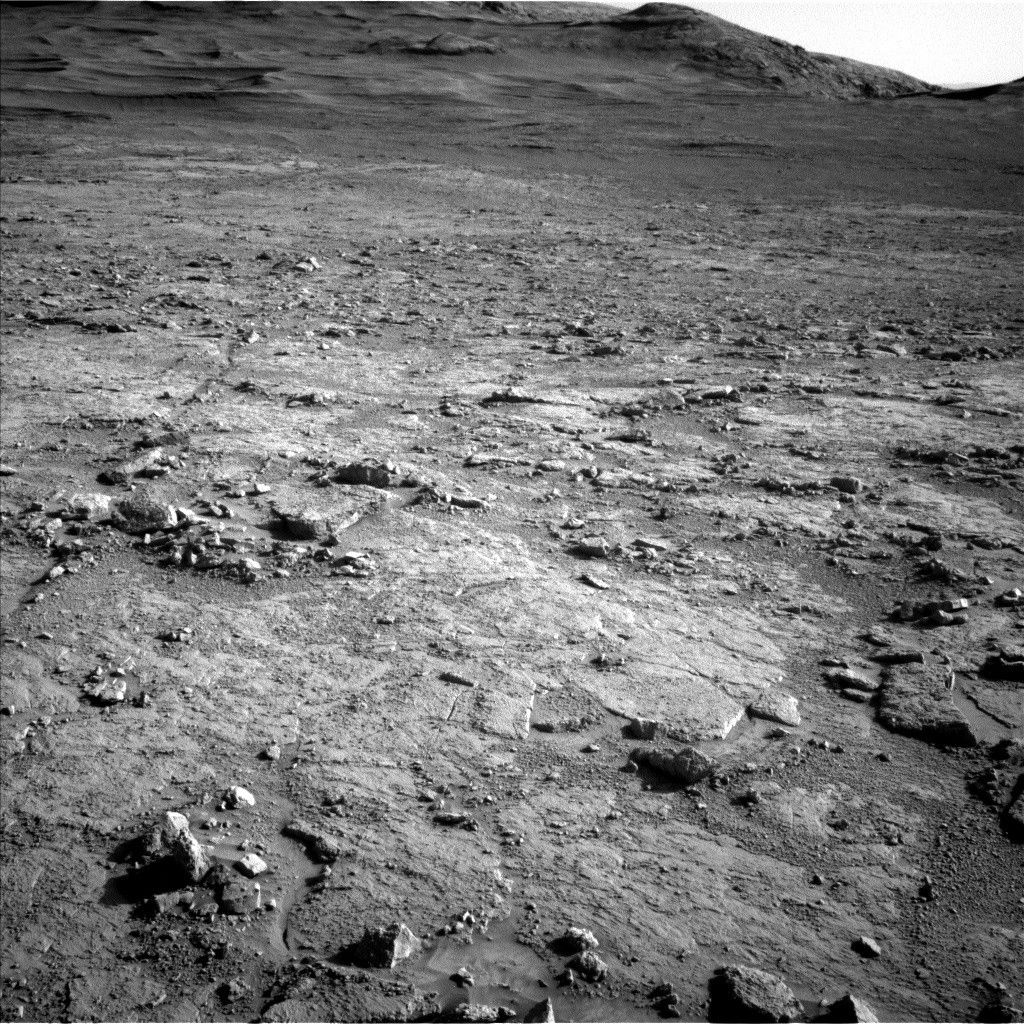
During the plan covering Sols 4575-4576, Curiosity continued our investigation of mysterious boxwork structures on the shoulders of Mount Sharp. After a successful 56-meter drive (about 184 feet), Curiosity is now parked in a trough cutting through a highly fractured region covered by linear features thought to be evidence of groundwater flow in the distant past of Mars. With all six wheels firmly planted on solid ground, our rover is ready for contact science! Unfortunately, a repeat of the frost-detection experiment expected for the weekend plan is postponed for a few days due to a well-understood ChemCam issue. In the meantime, our atmospheric investigations have a chance to shine, as they received additional time to observe the Martian sky.
In the early afternoon of Sol 4577, Curiosity’s navigation cameras will take a movie of the upper reaches of Aeolis Mons (Mount Sharp), hoping to see moving cloud shadows. This observation enables the team to calculate the altitude of clouds drifting over the peak. Next, Navcam will point straight up, to image cloud motion at the zenith and determine wind direction at their altitude. Mastcam will then do a series of small mosaics to study the rover workspace and features of the trough that Curiosity has entered. First is a 6×4 stereo mosaic of the workspace and the contact science targets “Copacabana” and “Copiapo.” The first target is a representative sample of the trough bedrock, and its name celebrates a town in Bolivia located on the shores of Lake Titicaca. The second target is a section of lighter-toned material, which may be associated with stripes or “veins” filling the many crosscutting fractures in the local stones. These are the deposits potentially left by groundwater intrusion long ago. The name “Copiapo” honors a silver mining city in the extremely dry Atacama desert of northern Chile. A second 6×3 Mastcam stereo mosaic will look at active cracks in the trough. Two additional 5×1 Mastcam stereo mosaics target “Ardamarca,” a ridge parallel to the trough walls, and a cliff exposing layers of rock at the base of “Mishe Mokwa” butte. At our current location, all the Curiosity target names are taken from the Uyuni geologic quadrangle named after the otherworldly lake bed and ephemeral lake high on the Bolivian altiplano, but the Mishe Mokwa butte is back in the Altadena quad, named for a popular hiking trail in the Santa Monica Mountains. After this lengthy science block, Curiosity will deploy its arm, brush the dust from Copacabana with the DRT, then image both it and Copiapo with the MAHLI microscopic imager. Overnight, APXS will determine the composition of these two targets.
Early in the morning of Sol 4578, Mastcam will take large 27×5 and 18×3 stereo mosaics of different parts of the trough, using morning light to highlight the terrain shadows. Later in the day, Navcam will do a 360 sky survey, determining phase function across the entire sky. A 25-meter drive (about 82 feet) will follow, and the post-drive imaging includes both a 360-degree Navcam panorama of our new location and an image of the ground under the rover with MARDI in the evening twilight. The next sol is all atmospheric science, with an extensive set of afternoon suprahorizon movies and a dust-devil survey for Navcam, as well as a Mastcam dust opacity observation. The final set of observations in this plan happens on the morning of Sol 4580 with more Navcam suprahorizon and zenith movies to observe clouds, a Navcam dust opacity measurement across Gale Crater, and a last Mastcam tau. On Monday, we expect to plan another drive and hope to return to the frost-detection experiment soon as we explore the boxwork canyons of Mars.